Mulawin Tree – A Gem of Philippine Forests
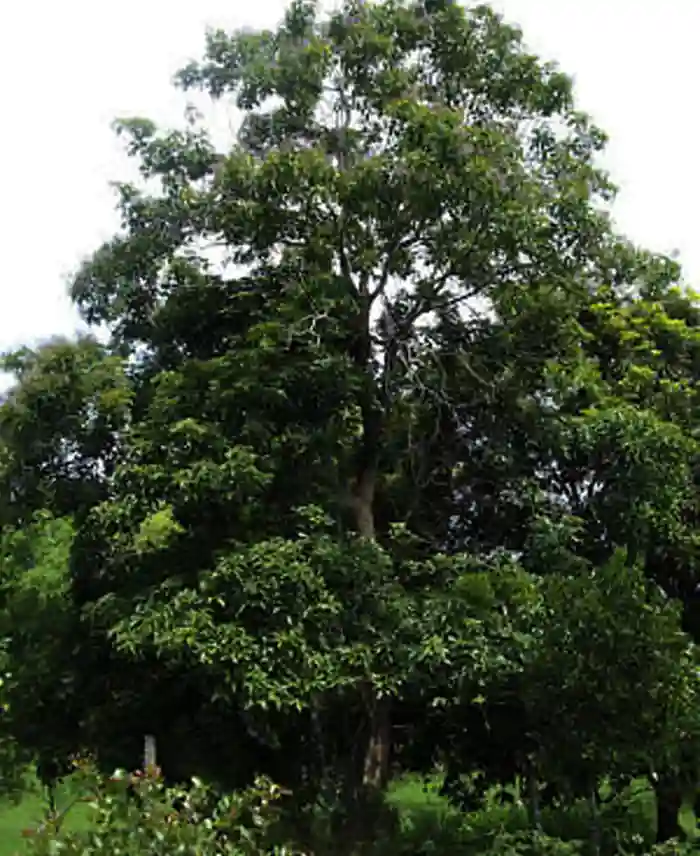

Nestled within the lush forests of the Philippines is a native tree that many may have heard of from folklore or fantasy TV shows—but few truly know in real life: the Mulawin tree. Also known as smallflower chastetree or the molave tree, scientifically:Vitex parviflora, the Mulawin is a strong, hardwood tree that plays a vital role in both ecological balance and cultural heritage.
A Tree of Strength and Beauty
The Mulawin tree is renowned for its durable and attractive wood. Belonging to the Lamiaceae family (the same family as mint and lavender), it stands tall and proud with its straight trunk and fine-grained hardwood that is prized for construction, furniture-making, and even boat-building.
Mulawin wood is highly resistant to termites and decay, making it a favorite for long-lasting structures. Historically, it was commonly used in building traditional Filipino homes and structures such as bahay kubo and bahay na bato.
Native Heritage
Found primarily in Luzon and parts of Mindanao, the Mulawin is an endemic species—meaning it naturally grows only in the Philippines. Unfortunately, this makes it vulnerable to deforestation and illegal logging. In fact, due to overharvesting, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has listed Vitex parviflora as a vulnerable species, highlighting the urgent need for conservation efforts.
Not Just Wood—A Tree with Healing Properties
Beyond its practical use in timber, parts of the Mulawin tree have been used in traditional medicine. Local communities have used bark extracts to treat minor ailments, though scientific research on its medicinal properties is still limited. Nevertheless, the tree is a valued component of the local ecosystem and indigenous knowledge.
Cultural and Mythological Roots
Many Filipinos may recognize the name “Mulawin” from the popular fantasy TV series of the same name. While the show took creative liberties, it helped bring attention to the tree and its mythical counterpart. In Philippine mythology, the Mulawin is sometimes associated with bird-like protectors of the forest, blending natural beauty with rich storytelling tradition.
Conservation and the Future
The survival of the Mulawin tree is closely tied to forest protection initiatives and sustainable forestry. Reforestation programs and increased awareness have helped restore some of its natural habitats. Organizations are now encouraging the cultivation of Mulawin in agroforestry projects, both to preserve biodiversity and to ensure a sustainable supply of hardwood.
Why We Should Care
Trees like the Mulawin are more than just resources—they are living legacies. They connect us to our environment, our culture, and our history. By learning more about the Mulawin tree and supporting conservation efforts, we help preserve a vital part of the Philippines’ natural heritage.
The next time you hear the word Mulawin, think beyond the TV screen. Picture the towering tree in the heart of the forest, rooted deeply in Philippine soil, history, and culture—waiting to be protected and appreciated.
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vitex_parviflora